LISSPI’s Business Solutions in 5 Stages
LISSPI’s Business Excellence Model guide Business Solutions at 5 most powerful stages, though these 5
stages appear work individually but in reality there are overlapping each other on some scenarios
and truly complimenting on each other. As a rule of thumb, the recommended order of application
would be;
0. Simple Logic & Intuitions
1. Lean Thinking Philosophy
2. Innovation & Creative Mindset
3. Six Sigma Statistical Studies and
4. Strategic Business Management

For the purpose of practical & ease of implementation and based on application, the LISSPI Business
Excellence Model has been further reclassified into 16 workable “Excellence Modules”.
Business Solutions – Stage 0 : Simple Logic & Intuitions
Foremost, LISSPI believes in strengthening the application of Simple Logic and People’s
Intuitions prior to applying any specific tools and techniques. It is also called “Common Sense”. Common Sense is
sound,practical judgement concerning everyday matters, or a basic ability to perceive, understand, and
judge in a manner that is common to all people. This help pluck “low hanging fruits”, is the first motivation for people to start recognize
their inner ability and power of people coming together for a common cause. Tangible returns may be meager
but intangible roots are mightier.
This stage is more fun filled as it allows people getting together, understanding each other,
improve the cohesiveness, quick wins, feel the power of (1.01)x , etc., as a result, transformation
begins
from
- Fixed Mindset to Fertile Mindset
- Command to Consensus
- Disbelieve to Believe
- Reluctance to Susceptive
- Insignificant to Infinite
- Exclusive to Inclusive
- Individualism to Collectivism etc.,
The ground getting prepared for real game change. Hence the sprouts of Transformation are
MIGHTIER one.

Business Solutions – Stage 1 : Lean Thinking Philosophy
Business Solutions – Stage 2 : Innovation & Creative Mindset
Business Solutions – Stage 3 : Six Sigma Statistical Studies
Business Solutions – Stage 4 : Strategic Business Management
L : Lean Thinking PhilosophyHolistic Approach, Continuous Learning, Empowering
Employees, Customer Orientation, Entrusting on Value Add, Creating Value Flow, Creating Capacity Tank,
Flexible to Accommodate Demand, Instill Servant Leadership, Waste Management , Quick Response finally,
More With Less.
I : Innovation Management taps the power of creative minds of middle management blended
with adaptation of technological upgradation brings leap jumps to foray. Innovation Management is what
makes the organisation ahead of rest of the industries.
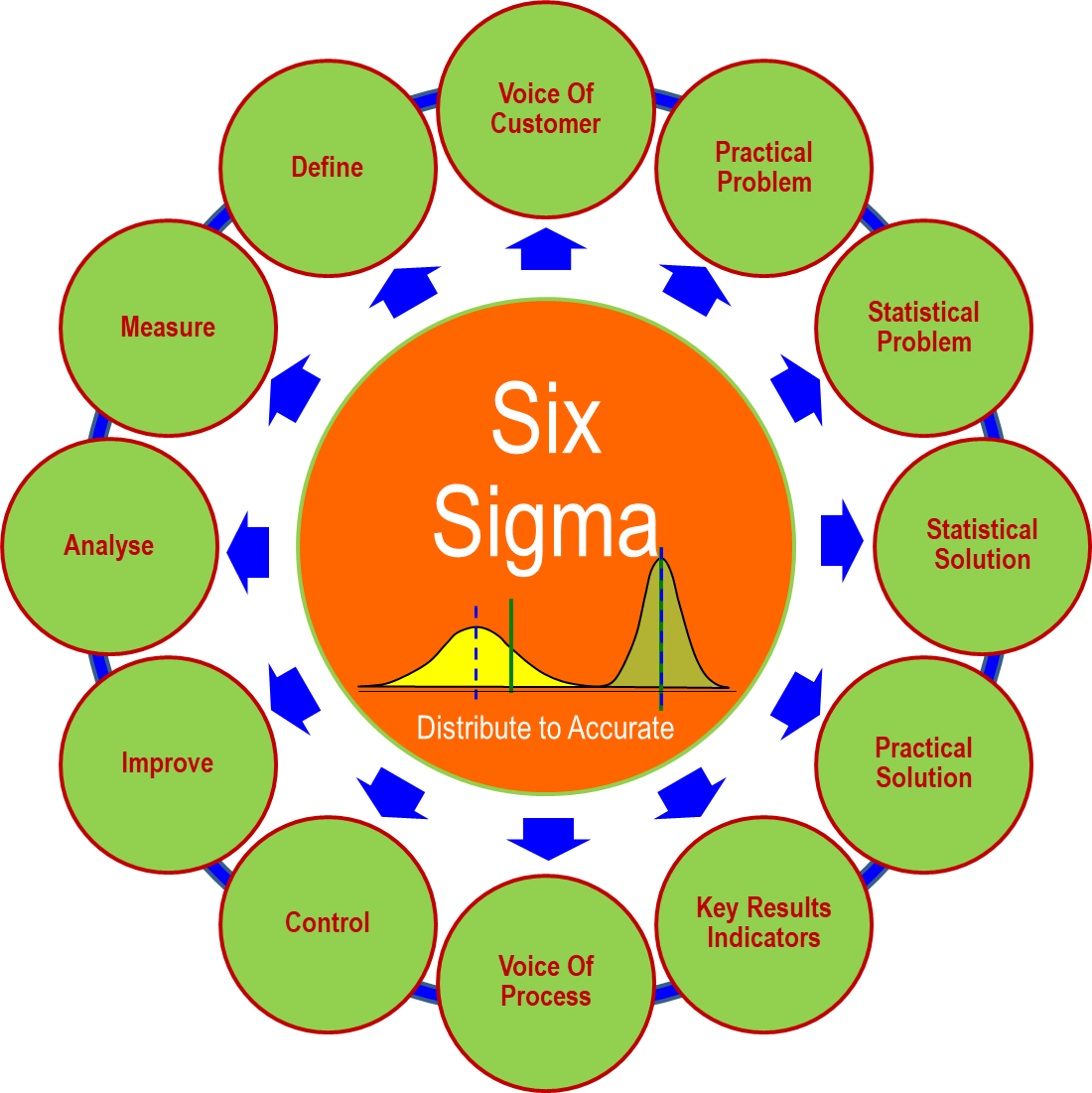
S : 6Sigma Statistical Analysis is a set of methodologies and tools used to improve
business processes by reducing defects and errors, minimizing variation, and increasing quality and
efficiency. The goal of Six Sigma is to achieve a level of quality that is nearly perfect, with only 3.4
defects per million opportunities.This is achieved by using a structured approach called DMAIC to
identify and eliminate causes of variation and improve processes.
S : Strategic Business Management is the process of formulating and implementing
initiatives to achieve an overarching business strategy. Strategic Business Management involves
measuring the success of an organization’s strategy over a period of time and making strategic decisions
that align the company’s strategy with its core competencies.
P : Practitioner any initiative shall be applied to see thereal pros and cons then to
get benefits out of it. So, it needs relentless practice, practice, practice but practice by
continuously applying hands-on tacit knowledge. Knowing is not Doing, Doing is Doing.
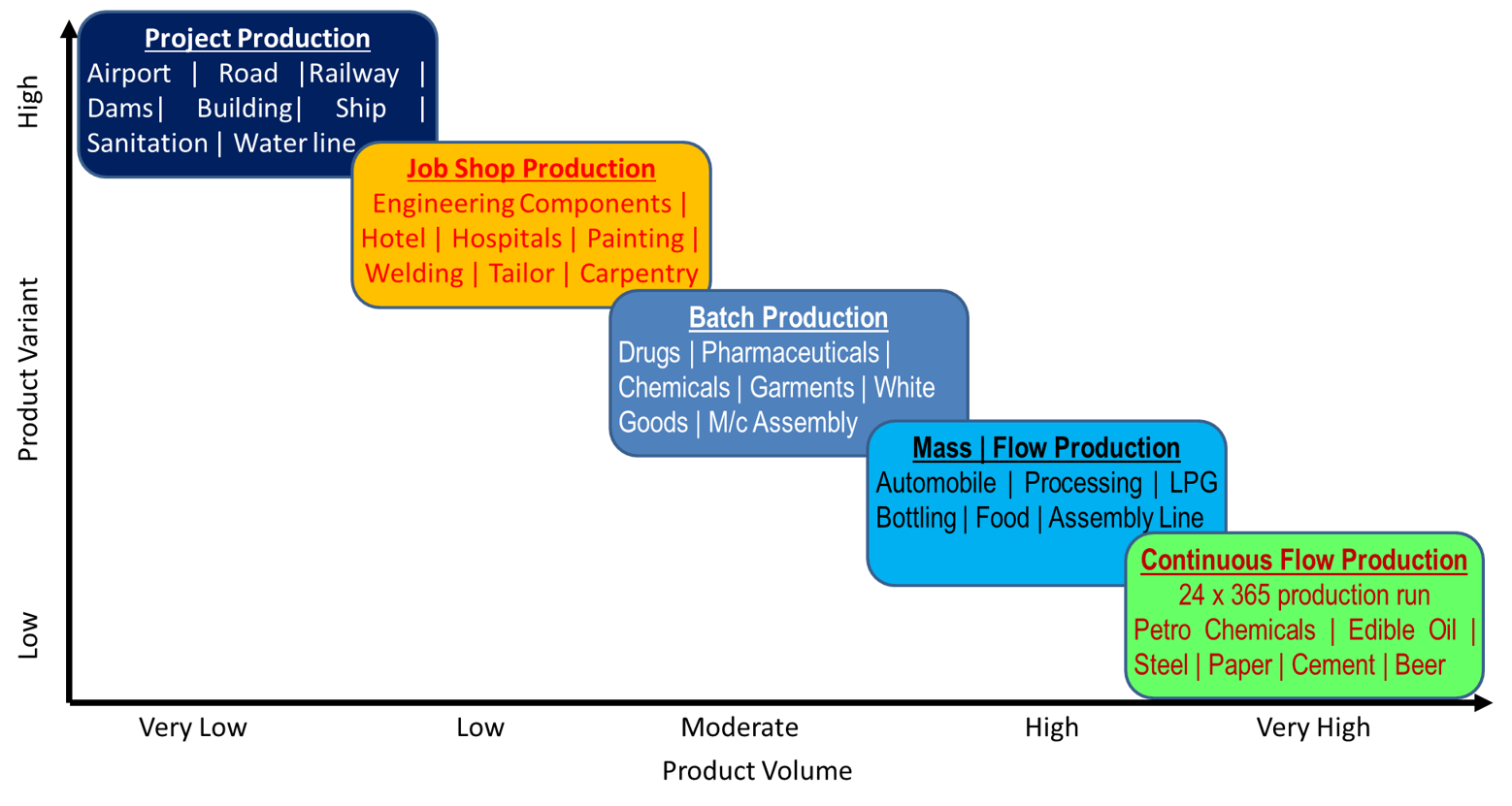
Nature of Customer’s Business
LISSPI do understand and value the nature of business you have undertaken and many times it is not
universal but unique. We develop customised solutions for you and make use of tools & techniques to the
intent possible, but not over using them.
Based on the business classification or placing to near to the one and having assessing your current
status; we offer the best suitable solutions at that point of time, then, go-on fine tuning them as
journey progresses.
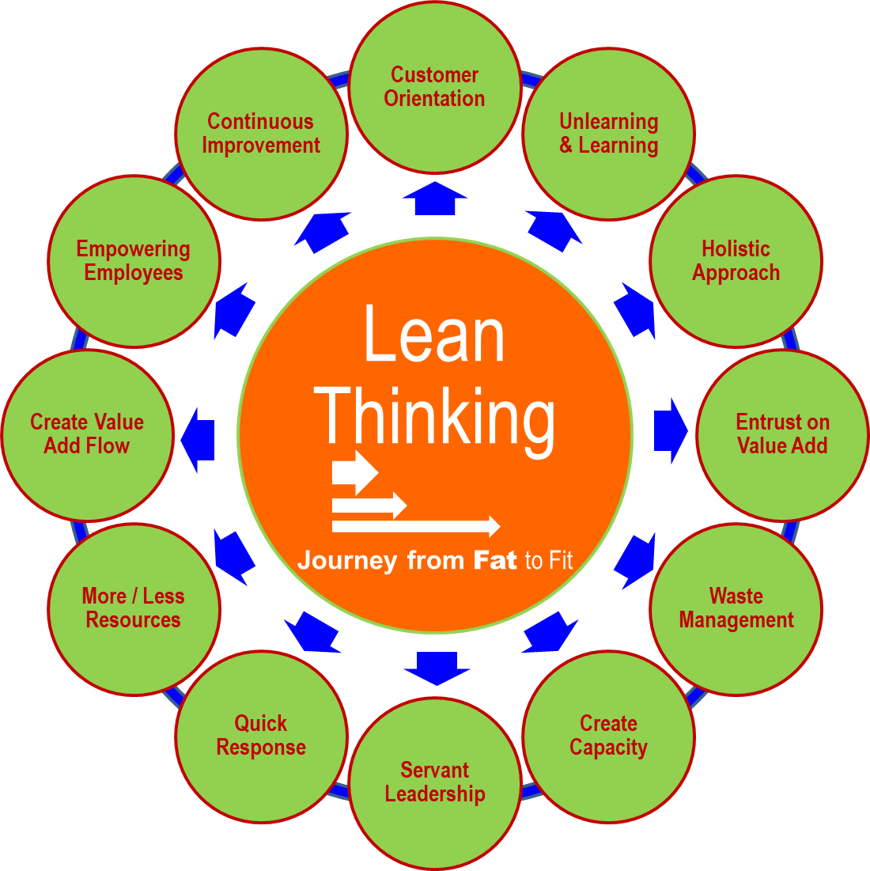
Lean Thinking Philosophy
Lean is an Illogical Thinking but Principle oriented Philosophy of doing work in certain
way. It is a systematic approach of identifying & eliminating waste through continuous improvement,
flowing the product at the pull of customer in pursuit of perfection”. Involve every employee of an
Organization and brought in cultural change to think alike towards a common goal.
Lean Thinking is an Holistic Approach, Continuous Learning, Empowering Employees, Customer
Orientation, Entrusting on Value Add, Creating Value Flow, Creating Capacity Tank, Flexible to
Accommodate Demand, Instill Servant Leadership, Waste Management , Quick Response finally,
More With Less.

Involve every employee of the organization by demonstrating leadership in
bringing
about a cultural change - to think alike and move towards a common goal i.e. Business
Excellence.
- Organised & Clean Work Place
- “0” High Level Process Mapping
- Andon
- Industiral Engineering
- Productive Maintenance
- Quick Change Over
- Managing Points & Checking Points
- Daily Work Management System
- Built-In-Quality
- Kaizen
- Train the Trainer
- Value Stream Mapping
- Value Stream Design
- Kanban
- Just In Time
- Basic QC Tools
- Change Management System
- Mistake Proofing
- Single Piece Flow
- Total Quality Management
- Jidoka
- Visual Management System
- Demand Flow Technique
- Heijunka - Levelled Production
- Takt Time
- Bottle Neck Management
- Gemba, Genichi, Gembitsu
- Hoshin Kanri
- Cellular Manufacturing
- Continuous Improvements
- Plan-Do-Check-Act
- Continuous Flow
- SMART Goals
- Standardised Work
- Team Work
- Total Employee Involvement
- Milkvan Run
- Zero Defect
- Statistical Process Control
- 8D Methodology
- A3 Report Writing
- Root Cause Analysis
- Theory of Constraints
- Advance Product Quality Plan
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis
- Balanced Score Card
- Industrial Safety
- Key Process Indicators
- Strategic Management Tools
- Measurement System Analysis
- Risk Analysis / Risk Management
- Project Management
- Quality Control Circles
- Multi Skill
6 Sigma Statistical Analysis
Six Sigma Statistical Analysis navigates towards hidden tumbling blocks and hidden root causes. This
enhances robust product & process design capability and also people’s complex problems solving ability.
6 Sigma Statistical Analysis is a set of methodology and tools used to improve business processes by
reducing defects and errors, minimizing variation, and increasing quality and efficiency. The goal of
Six Sigma is to achieve a level of quality that is nearly perfect, with only 3.4 defects per million
opportunities. This is achieved by using a structured approach called DMAIC to identify and eliminate
causes of variation and improve processes.
- Project Scope
- Project Charter
- Business Impact
- Bench Marking
- Voice of Customer
- SIPOC
- Affinity Diagram
- Kano’s Model
- CTQ Tree
- “0” Level Proc Map
- Data Collection
- Confidence Interval
- Process Capability
- Nominal Group Technique
- MSA
- Yields (RTY)
- Normality Test
- GR&R
- Chi-Square
- Multi Vary Analysis
- Hypothesis Testing
- E-Test/F-Test
- Histogram
- Co-relation Regression
- T-Test
- ANOVA
- Noise Variables
- Scatter Plots
- Design Of Experiments
- Tolerance Analysis
- Alpha & Beta Risk
- Centre Points
- Design For Six Sigma
- Design Of Experiments
- Theory Of Constraints
- Full Factorial
- Fractional Factorial
- Response Surface
- Evolutionary Operations
- Capability Studies
- Multiple Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Auto Co-relation
- Attribute Response
- Sequential Experimentation
- MSA
- Control Charts
- Statistical Control
- Control Plan
- Reaction Plan
Strategic Business Management
Strategies guide business to grow and run efficiently
Strategic Business Management put the Organisation
Leadership into litmus test for their ability to foresee the future and to set the compass now.
Strategic Business Management compel to align Organisational Goals and Objectives at every level.
Strategy Business Management is the process of Analysis, Formulating, Executing,
utilization of resources through competition analysis, Implementing the defined goals and Objectives
and achieve an overarching business results. Includes a consideration of Internal Processes &
External Factors impacting the business.
Strategic Business Management involves measuring the success of an organization’s
strategy over a period of time and making strategic decisions that align the company’s strategy with
its core competencies. Strategic business management relies mainly on research and planning, which
is essential for any company to succeed in their home market as well as in the international
business space.
Any strategy that is not centered on the people is doomed to fail!
Many Strategies Fail Because They’re Not Actually Strategies.
Mainly, there are five types of Strategic Business Management
- Linear Strategic Business Management.
- Adaptive Strategic Business Management.
- Interpretive Strategic Business Management.
- Expressive Strategic Business Management.
- Transcendent Strategic Business Management.
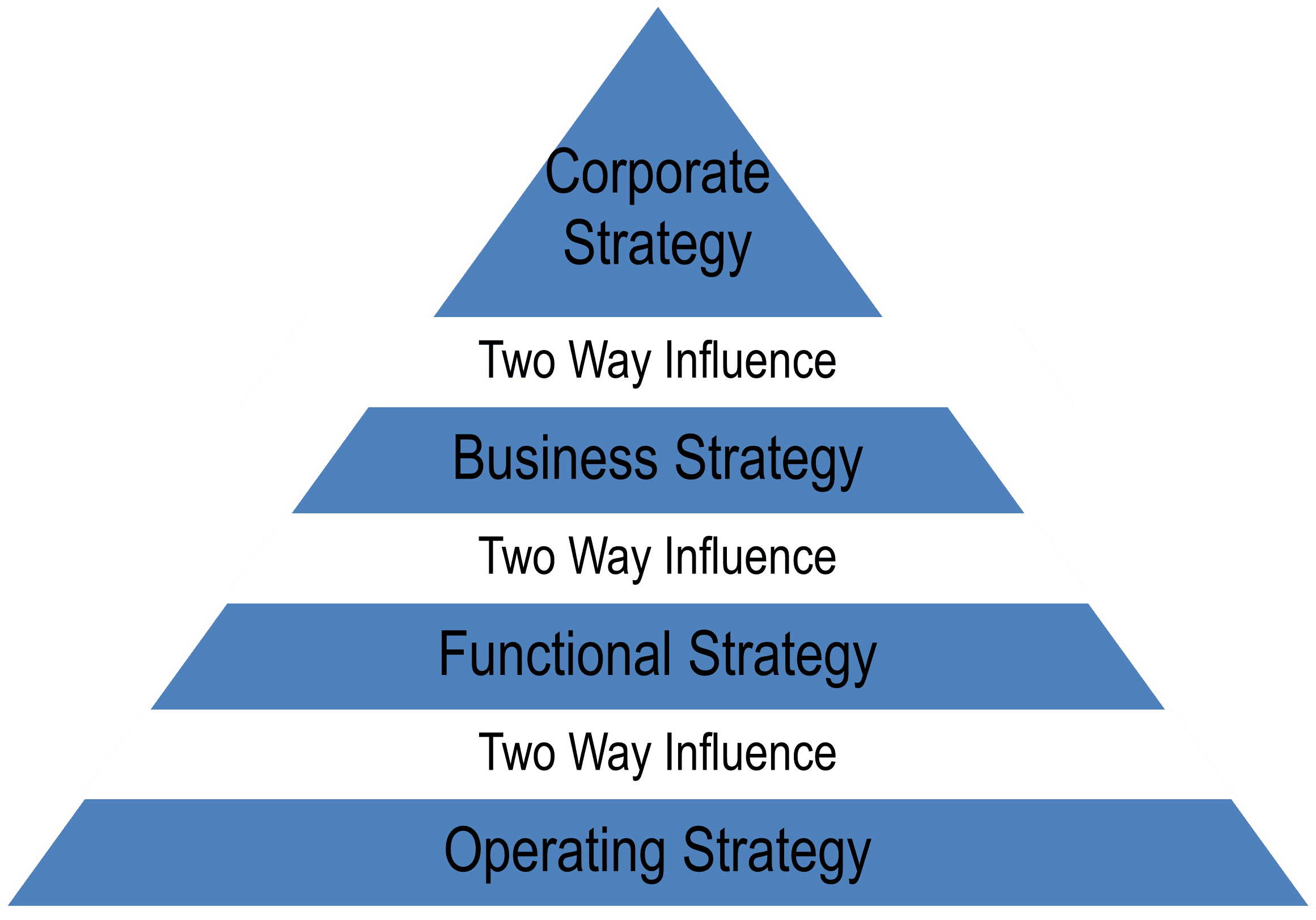
Incorporating Strategic Business Management is to gain a competitive advantage
over the market. Strategy could be at one or at all 4 levels as the case may be.
Steps involved in Strategic
Business Management:
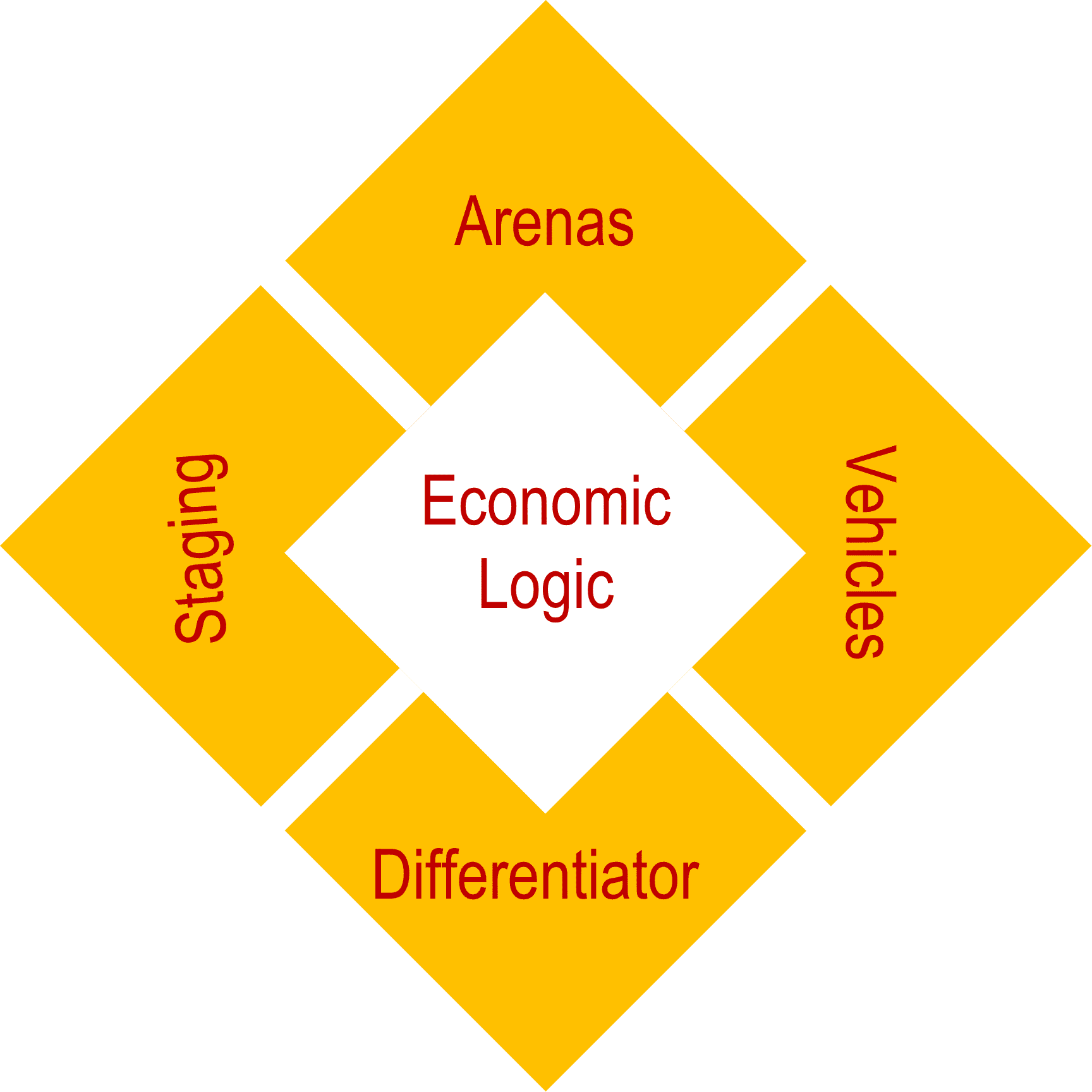
An effective strategy essentially contains
interrelated Arenas, Differentiators, Vehicles, Staging, and Economic Logic. Each of these
five elements are interrelated and mutually reinforcing in the Strategy Diamond Model.
- Arenas: What do we plan to achieve? What is the nature of our products, services,
distribution channels, and market segments? What geographic areas do we plan to expand
into? What technologies will we use?
- Differentiators: What sets us apart from our competition? Is it an image, price,
product dependability, and how quickly we get our product to the marketplace? How will
we win the marketplace?
- Vehicles: How will we get there? Will we get there through strategic alliances?
Development? Licensing?
- Staging: How will we advance our product or positioning? How quickly will we
move? In what order we will move forward
- Economic logic: How will we obtain our returns? Will this be achieved by lowering
costs to give value for the price? Providing premium services for premium pricing?
Strategy Analysis Tools
- GAP Analysis
- VIRO Analysis
- Four Corners Analysis
- Value Chain Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Force Field Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
Strategy Formulating Tools
- VISION | MISSION | VALUES
- Business Growth Strategy
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- McKinsey 7S Framework
- Ansoff | BCG | GE Matrix
Strategy Execution Tools
- Policy Deployment
- Managing Point & Checking Point (Vertical Integration)
- Cross Functional Teams
- Horizontal Deployment (Horizontal Integration)
- Daily Work Management
Strategy Analysis Tools
- Key Result Areas
- Key Performance Indicators
- Key Process Indicators
Strategy Analysis Tools
- Benchmarking
- Balanced Score Card
“X” Business Excellence Model
LISSPI do understand and value the nature of business you have undertaken and many times it is not
universal but unique. Based on the business classification or placing business to near to the one and
having assessing current culture & strategy, we support evolving your own Business Excellence Model
which suits best at this point of time, then, go-on fine tuning them as journey progresses.